Atmospheric rivers trigger melting in West Antarctica
Press release published by Univ. Grenoble Alpes / CNRS / Sorbonne Université

The ice flow transported to the ocean through the Antarctic ice shelves represent 80% of the total Antarctica ice output. These ice shelves are confined in huge bays and, like the cork of a bottle of sparkling wine, hold the Antarctic glaciers by a buttressing effect which transfers upstream the friction along the edges and from contact with oceanic rock outcrops. The disintegration of these ice shelves leads to a massive acceleration of the glaciers that are normally restrained. Once they are no longer restrained, they go to the ocean just as the sparkling wine pours away after the ejection of the cork.
Over the past couple decades, the successive break-ups of the Larsen A, Larsen B, and recently the Larsen C ice shelves demonstrated that the occurrence of surface melting on the ice shelves is critical in initiating their collapses. After the snow surface becomes saturated, water collects in lakes and eventually fill crevasses. As the density of the liquid water is higher than the solid, an overpressure forms at the bottom of the crevasse causing it to expand in a process known as hydrofracturing.
Many studies have focused on the local processes that cause snow and ice melt. Also, the positive feedback between snow melt and decreased snow albedo [2] along with the impact of the foehn wind on surface warming is well documented. However, until now, there had been no studies to understand the climatological of these large-scale meteorological conditions that caused this surface melting in the Antarctic. This new analysis revealed that atmospheric rivers frequently play a significant role in these melt events.
Atmospheric rivers represent narrow bands of moisture that travel from the tropical regions towards higher latitudes. The extra-tropical cyclones that circle the Antarctic continent deliver atmospheric rivers onto the continent when the polar jet stream becomes highly wavy. When the rivers make landfall, they deliver an intense plume of heat and moisture over a small area. These rivers have been extensively studied in more temperate climates where they associated with rainfall and flooding, but there are only a few studies of their impacts over Antarctica one of which connects rivers with high snowfall events in East Antarctica.
Scientists have analyzed all atmospheric river activity in West Antarctica and the Antarctic Peninsula since 1980. They have shown that the majority of melt events on the large Ross Ice Shelf are triggered by the arrival of an atmospheric river (Figure 1a). Similarly, they even found large-scale melt events on the Antarctic Peninsula triggered by atmospheric rivers during the darkness of winter (Figure 1b).
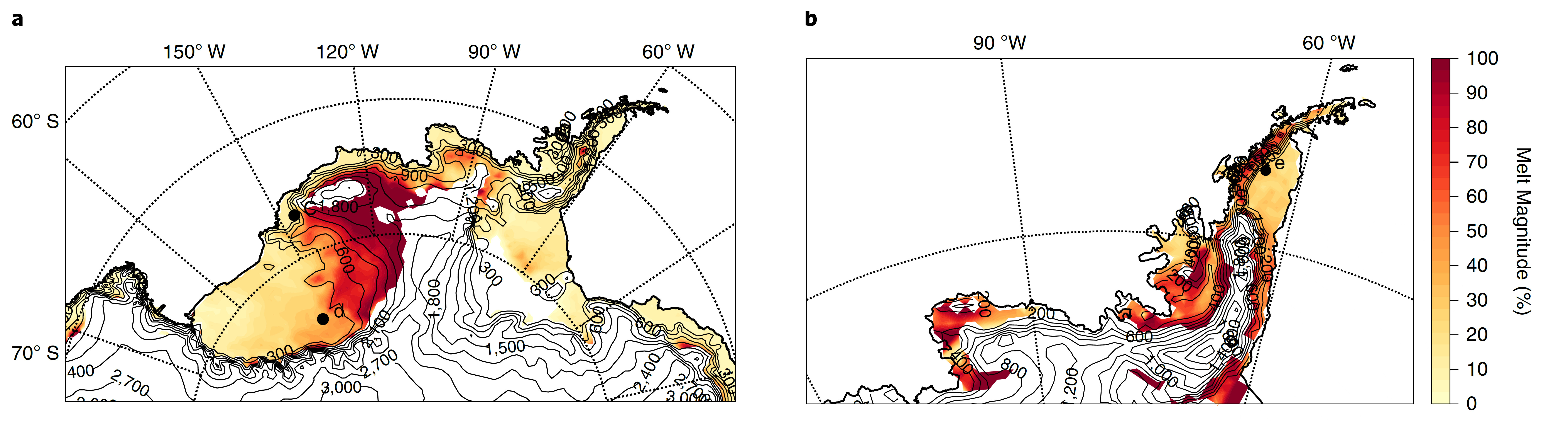
The analysis showed that atmospheric rivers are able to reach the Antarctic when extra-tropical cyclones are blocked from moving in their normal west to east path by an anticyclone and instead the humidity they carry is forced southward (Figure 2). When a cyclone encounters a blocking anticyclone, the atmospheric river is forced down a single path, like a pizza dough flattened between two rotating rollers. The river carries heat and humidity that originated from more temperate regions down an “atmospheric channel” makes landfall on the Antarctic coastline and causes abnormally warm conditions (+10 ° C above normal). When the river reaches Antarctica, the melting is triggered by the strong downward longwave radiation that is caused by the darker clouds carrying liquid water over the ice sheet.
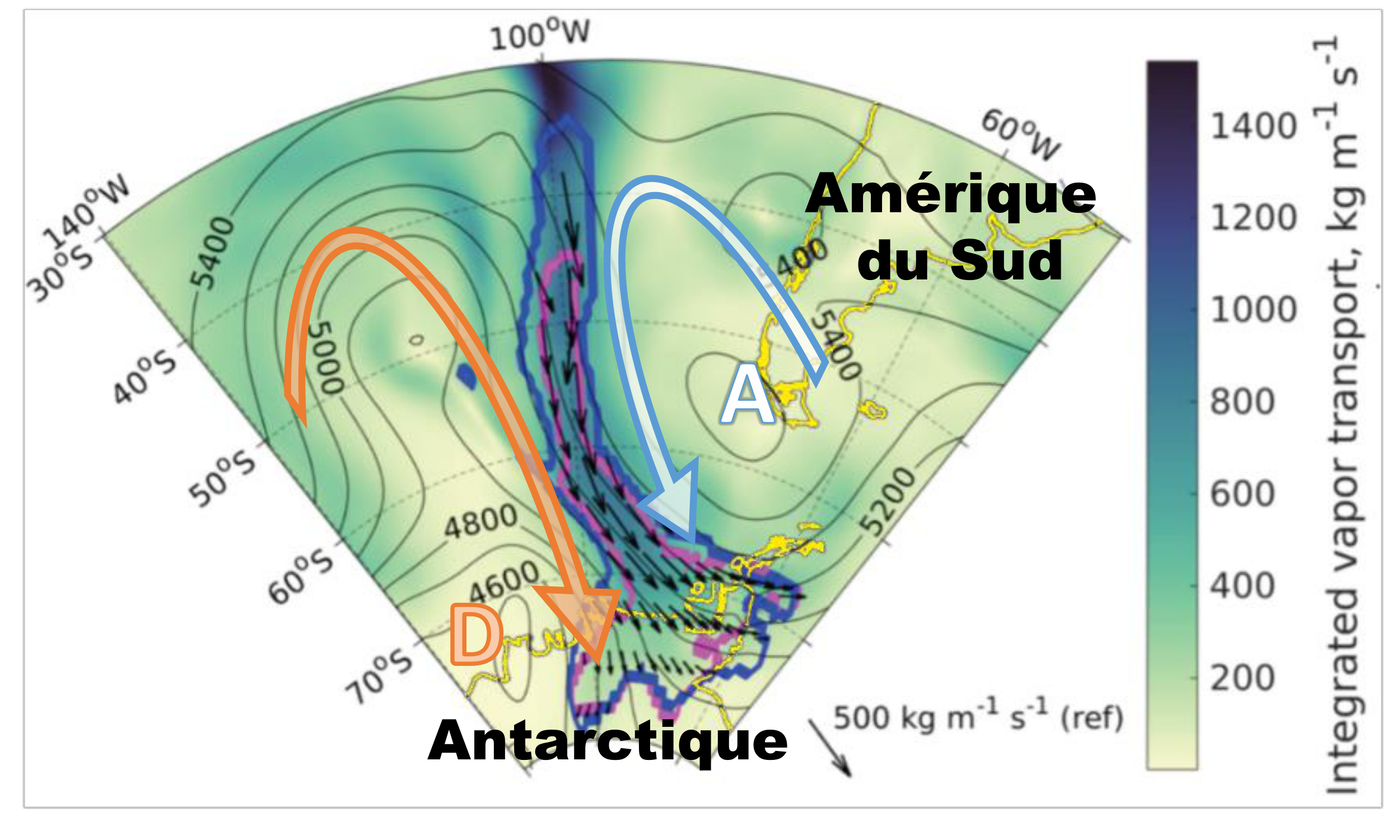
Research has shown that only the warmest atmospheric rivers are associated with melt events on the ice shelves. Nevertheless, those warmest rivers are only 2 °C warmer than the average river. In the context of climate change, warming over the Ross Ice Shelf is expected to exceed 2 °C by the end of the 21st century. This would lead to the majority of atmospheric rivers causing large-scale melting on the ice shelves on a near annual basis, jeopardizing their stability. Since the frequency of atmospheric river landfalls over West Antarctica has also increased slightly since 1980, it is now essential to focus on the origin of the blocking anticyclones that direct rivers towards Antarctica and analyze their evolution in a warming climate.
Référence
West Antarctic surface melt triggered by atmospheric rivers, Jonathan D. Wille, Vincent Favier, Ambroise Dufour, Irina V. Gorodetskaya, John Turner, Cécile Agosta & Francis Codron Nature Geoscience, 28 October 2019, DOI: 10.1038/s41561-019-0460-1
Researcher contacts
– Vincent Favier, IGE / OSUG, | vincent.favier univ-grenoble-alpes.fr
– Jonathan Wille, IGE / OSUG | jonathan.wille univ-grenoble-alpes.fr
Publié le 29 octobre 2019
Updated on 29 October 2019
[1] IGE - Institut des géosciences de l’environnement, CNRS/UGA/IRD/Grenoble INP, Saint Martin d’Hères, France
CESAM - Centre for Environmental and Marine Studies, Department of Physics, University of Aveiro, Portugal
British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge, UK
LSCE - Laboratoire des sciences du climat et l’environnement, UVSQ/CNRS/CEA, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
LOCEAN - Laboratoire d’océanographie et du climat : expérimentations et approches numériques, Sorbonne Université, MNHN/CNRS/IRD/, France
[2] Albedo is the proportion of shortwave radiation that is reflected by a surface like snow
 Intranet
Intranet









